Android — is an operating system (OS) created and developed by Google, which dominates the smartphone and tablet market. In this article, we will take a detailed look at the history of Android, its architecture, as well as the principle of operation and use.

- Who invented Android
- What language is Android written in
- Main Android programming languages:
- What kernel is the Android kernel based on?
- Android Architecture
- How Android Works
- How to use Android
- Comparison with other mobile operating systems
- A quick comparison of Android with these operating systems:
- Android
- iOS (Apple):
- Windows Mobile (Microsoft):
- Questions on the topic
- What alternative mobile operating systems are there on the market besides Android, iOS and Windows Mobile?
- How do I update my device to the latest Android version?
- What are the main differences between the different versions of Android?
- Which version of Android is best for my device?
- How can you optimize the performance and battery life of your Android device?
- How to protect your Android device from viruses and malware?
- What are the best Android apps and games to install?
- How to set up parental controls on an Android device?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of using Android devices compared to devices on other platforms?
- Which manufacturers make the best Android devices, and how to choose the right smartphone or tablet?
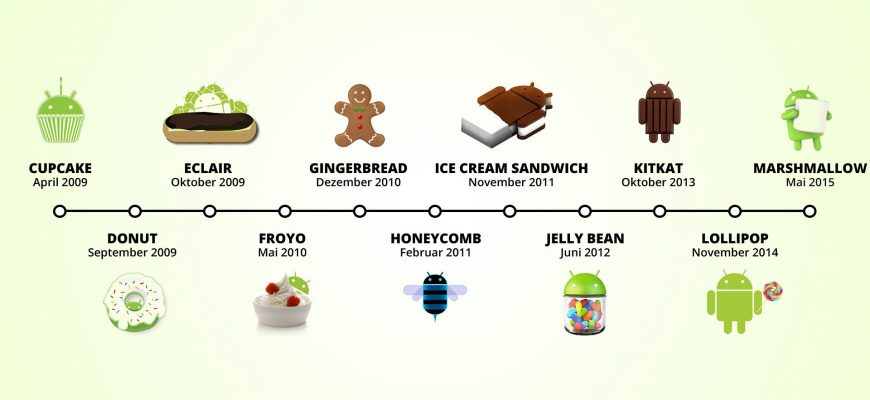
Who invented Android
Android Inc. was founded in October 2003 by Andy Rubin, Rich Miner, Nick Sears, and Chris White with the initial idea of developing a smart operating system for cameras. However, they soon changed the focus of their project to developing an OS for mobile devices that could compete with Symbian and Microsoft Windows Mobile.
In 2005, Google acquired Android Inc., and Andy Rubin became the head of mobile platform development at the company. The first smartphone with the Android operating system hit the market in 2008 - it was the HTC Dream (T-Mobile G1). Since then, Android has taken a leading position in the mobile device market, and as of 2021, Android's market share is about 72%.
What language is Android written in
Android is written in several programming languages. The main development languages for Android are Java and Kotlin. Kotlin has been the official development language of Android since May 2017. Most applications on the Android platform are developed in these two languages.

However, some parts of the operating system are written in C and C++. These languages are used to write low-level components such as device drivers and to optimize performance.
Main Android programming languages:
- Java
- Kotlin
- C
- C++
What kernel is the Android kernel based on?

The Android operating system kernel is based on the Linux kernel. Linux is open and freeopen source code, allowing developers to modify and adapt it to their needs. In particular, Android uses a modified version of the Linux kernel optimized for mobile devices and tablets.
Android is based on long-term supported (LTS) versions of the Linux kernel, which helps maintain stability and security. Over time, Google actively collaborates with Linux kernel developers to introduce new features, improve performance, and support new hardware.
Android Architecture
The Android architecture consists of several layers:
- Linux Kernel: At the lowest level of the architecture is the Linux kernel, which provides basic functionality such as resource management, device drivers, and interaction with hardware.
- Libraries and Android Runtime: This level contains native libraries written in C and C++, as well as Android Runtime (ART), which is responsible for executing application code.
- Framework: A layer that contains the core components of a system and the APIs for developing applications.
- Applications: At the top level are user applications and system services.
Table 1. Main components of Android architecture
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Linux kernel | Resource management, device drivers, interaction with hardware |
| Libraries and ART | Native libraries, application code execution |
| Framework | Main system components and API for application development |
| Applications | User applications and system services |
How Android Works
Android runs on a virtual machine system called the Android Runtime (ART), which executes application code. ART uses Just-In-Time (JIT) or Ahead-Of-Time (AOT) compilation to convert application source code into machine code that can be executed by the device's processor.
The Android operating system is multitasking, which means it allows multiple applications to run simultaneously. To efficiently manage resources and prevent memory leaks, Android uses a garbage collector system that automatically frees up memory occupied by unused objects.
One of the key features of Android is its modularity and flexibility. The system supports a wide range of hardware platforms and configurations, allowing manufacturers to tailor the OS to their devices. In addition, users can customize their experience by installing a variety of apps and widgets, as well as changing the appearance of the interface.
How to use Android
To use Android, you need to know the basic principles of working with the operating system and its interface. Here are some basic controls and functions:
- Home screen: The main screen of your device, where app shortcuts, widgets, and folders are located.
- Notification panel: Swipe down from the top of the screen to open the notification panel, where you can see important information such as missed calls, messages, and app notifications.
- Quick Settings: Swipe down from the top of the screen twice or with two fingers at the same time to open the Quick Settings panel, where you can turn on or off features like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GPS, and more.
- Apps menu: Tapping the Apps icon or swiping up from the bottom of the screen opens a menu with all installed apps.
- Multitasking: The Recent Apps button or swipe up and then left to switch between active apps or close them.
Comparison with other mobile operating systems
Android is not the only mobile operating system on the market. It competes with systems such as Apple's iOS and Microsoft's Windows Mobile.
A quick comparison of Android with these operating systems:
Android
- Open and modular architecture
- A wide variety of devices and manufacturers
- Wide selection of applications and games
- Flexible customization of interface and functionality
iOS (Apple):
- Closed and controlled architecture
- Limited number of devices (iPhone and iPad only)
- High quality applications and games
- Great emphasis on security and privacy of user data
Windows Mobile (Microsoft):
- Closed architecture with focus on integration with Microsoft ecosystem
- Limited number of devices and manufacturers
- Fewer apps and games available
- Deep integration with Microsoft services such as Office and OneDrive
Android is one of the most popular mobile operating systems that offers flexibility, openness and a wide range of features for users and developers. In this article, we have covered the main aspects related to the history of Android, its architecture, principles of operation and use, and also compared it with other mobile operating systems.
Android is one of the most popular mobile operating systems that offers flexibility, openness and a wide range of features for users and developers. In this article, we have covered the main aspects related to the history of Android, its architecture, principles of operation and use, and also compared it with other mobile operating systems.
Questions on the topic
What alternative mobile operating systems are there on the market besides Android, iOS and Windows Mobile?
Alternatives: KaiOS, Sailfish OS, Tizen, Ubuntu Touch, LineageOS and HarmonyOS.
How do I update my device to the latest Android version?
Update: Check for updates in your device settings, under About or System.
What are the main differences between the different versions of Android?
Differences between versions: Each version of Android brings improvements in performance, security, new features and interface design.
Which version of Android is best for my device?
Best version: Depends on your device and manufacturer support. Generally, you should use the latest version available.
How can you optimize the performance and battery life of your Android device?
Optimization: Remove unnecessary applications, limit auto-loading, enable power saving mode and update software.
How to protect your Android device from viruses and malware?
Protection: Install applications only from the official store, use antivirus and update the system regularly.
What are the best Android apps and games to install?
Top Apps and Games: Depends on your preferences and needs. Google Play has top lists of popular apps and games.
How to set up parental controls on an Android device?
Parental controls: Use dedicated apps or the Family Sharing feature in Google Play.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using Android devices compared to devices on other platforms?
Pros and cons: Android offers flexibility, openness, and device diversity. Cons include lower stability and security than iOS.
Which manufacturers make the best Android devices, and how to choose the right smartphone or tablet?
Top manufacturers: Samsung, Google, OnePlus, Xiaomi and others. The choice depends on the budget, preferences and required characteristics.